What is Enterprise Scrum?
Enterprise Scrum is an adaptation and extension of Scrum based on abstraction, generalization, and parameterization; that can be used in a scaled generic way for any management purpose.
The goal of the Enterprise Scrum is to grow unicorns and transform dinosaurs into unicorns. In other words, Enterprise Scrum powers DISRUPTION and allows companies of all sizes to be managed like startups which can simultaneously act like VCs as they grow up.
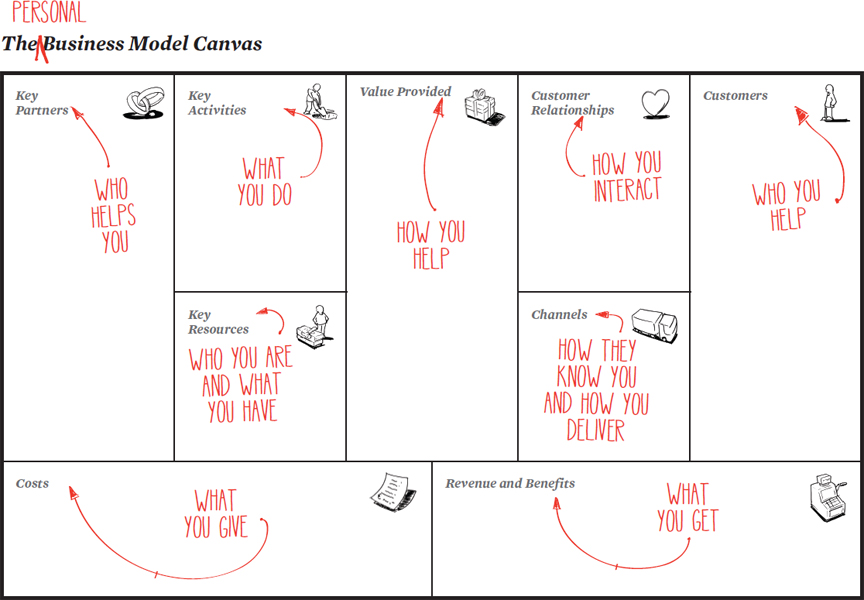
Many of the Roles and Artifacts in Enterprise Scrum are named differently to not confuse other business people with the word "product".
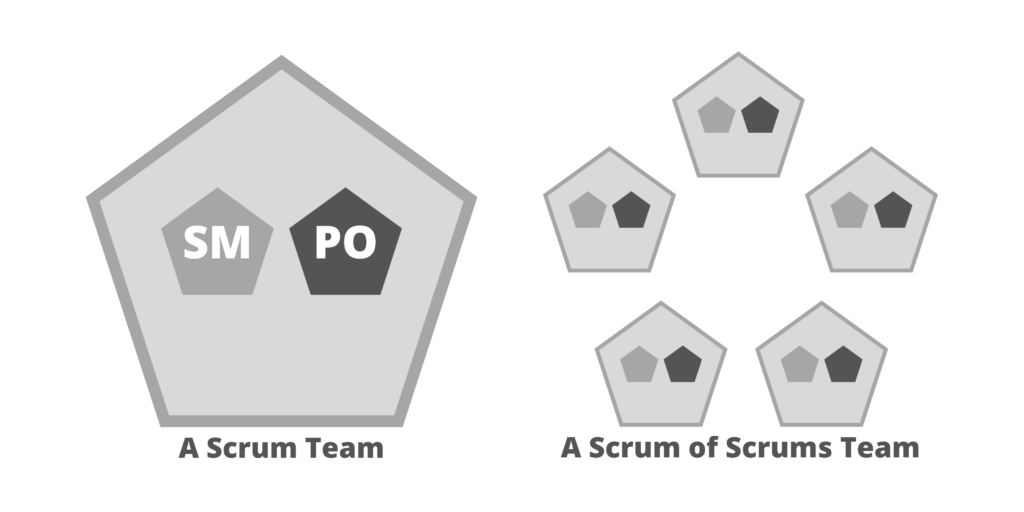
Roles
- Business Owner. Used instead of the Product Owner (PO) role.
- Coach. Used instead of the Scrum Master (SM) role.
- Team. It is still the Team.
Business Value
- It is defined explicitly through a balance of the metrics (see below).
Artifacts
- Value List. Used instead of "Product Backlog".
- A list of things that when DONE add value.
- Value List Items (VLIs). Instead of Product Backlog Items (PBIs).
- Each of them with a DOR, DOD, and other attributes.
- VLIs are DONE according to their DOD every Cycle.
- Projections
- These are made with measurements over metrics of what got DONE (see below), so Release Planning is naturally included for all Cycles and at all levels.
Events
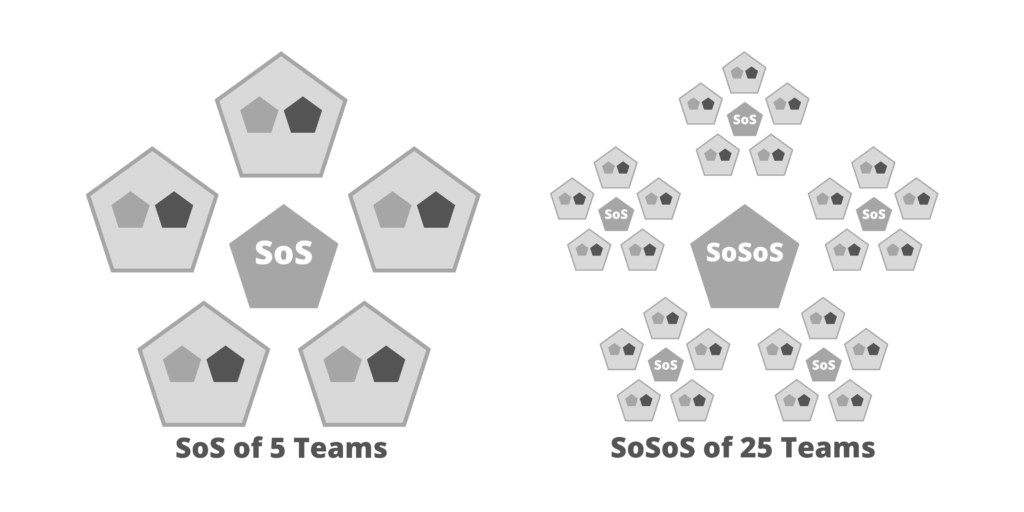
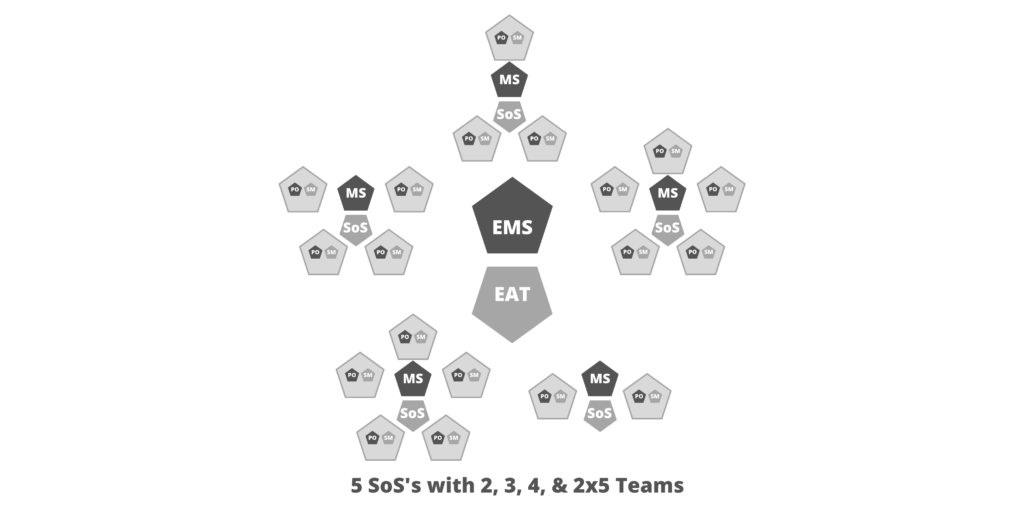
- Cycle. Used instead of Sprints.
- Cycles can be recursive without limit.
- You can have a yearly cycle, a quarterly cycle, or a 2-week cycle.
Techniques
- Techniques of different types and at different levels can be included with specific parameters and inserted as 1) new steps, 2) to get work done into the framework relevant to the purpose of the instance (see below).
- For example, techniques can be added for 1) facilitating work like User Stories, or 2) insertable NEW steps in an instance like Release Planning, or Architectural Scan added as NEW activities in the Initial Value List/Wave Projection.
Metrics and Reports
- The only mandated report is the ScrumBoard.
- In contrast with Scrum with 1 metric, the velocity, in Enterprise Scrum we are FREE to have as many metrics as you want/need. For example, we could track, profit, revenue, incidents, effort, customer satisfaction, compliance levels, etc.
- In contrast with Scrum where we have the Burn down charts, in Enterprise Scrum you are FREE to choose any type of report.
Other Parameters
- Enterprise Scrum also provides 80+ other parameters to extend, customize and apply the Scrum concepts to different domains, scaling, or adding techniques.
- These parameters were abstracted primarily by observing what people had already done in the field as they used Scrum for different purposes.
- These parameters make Enterprise Scrum a true framework, as the customizable parts are now visible and explicit. (I will release the full list of parameters later as a different publication.)
Instances
- The framework exists as an explicitly customizable tool, but once the parameters, techniques, and added steps have been chosen, a defined Enterprise Scrum instance is created explicitly. For example, there are instances like:
- the instance of Enterprise Scrum with User Stories and Release Planning.
- the instance of Enterprise Scrum for Marketing.
- the instance of Enterprise Scrum for Compliance Management.
- the instance of Enterprise Scrum for Real State Sales.
- the instance of Enterprise Scrum for Business Unit Portfolio management.
The Wave Principle
- Any long-term "rough" predictions made in the Initial Value List of a longer Cycle, must be refined or recalculated after each and every shorter Cycle it includes.